Как работает автоматическое сканирование IT-инфраструктуры в GINC RADAR
Когда в компании десятки проектов, сотни репозиториев и десятки тысяч строк кода, очень сложно ответить на простой вопрос: а какие именно технологии мы используем?
Удивительно, но даже в крупных IT-компаниях ответ на этот вопрос часто строится на устаревших Excel-таблицах, ручных опросах команд и догадках архитекторов. Проблема в том, что реальная картина сильно отличается от того, что указано “на бумаге”.
GINC RADAR решает эту задачу иначе — с помощью автоматического сканирования IT-инфраструктуры. Ниже расскажем подробнее, как это работает, и почему это превращается в стратегический инструмент для CTO, архитекторов и тимлидов.
Почему ручной аудит не работает
Ручные подходы к учету технологий страдают сразу несколькими недостатками:
Неактуальность: список технологий устаревает буквально через месяц. Новые библиотеки появляются каждый день.
Человеческий фактор: разработчики могут забыть упомянуть используемый пакет, указать неточную версию или вовсе не заметить дублирование.
Высокие затраты: опросы, сведение таблиц и сверки занимают недели и отвлекают специалистов от основной работы.
Как GINC RADAR сканирует инфраструктуру
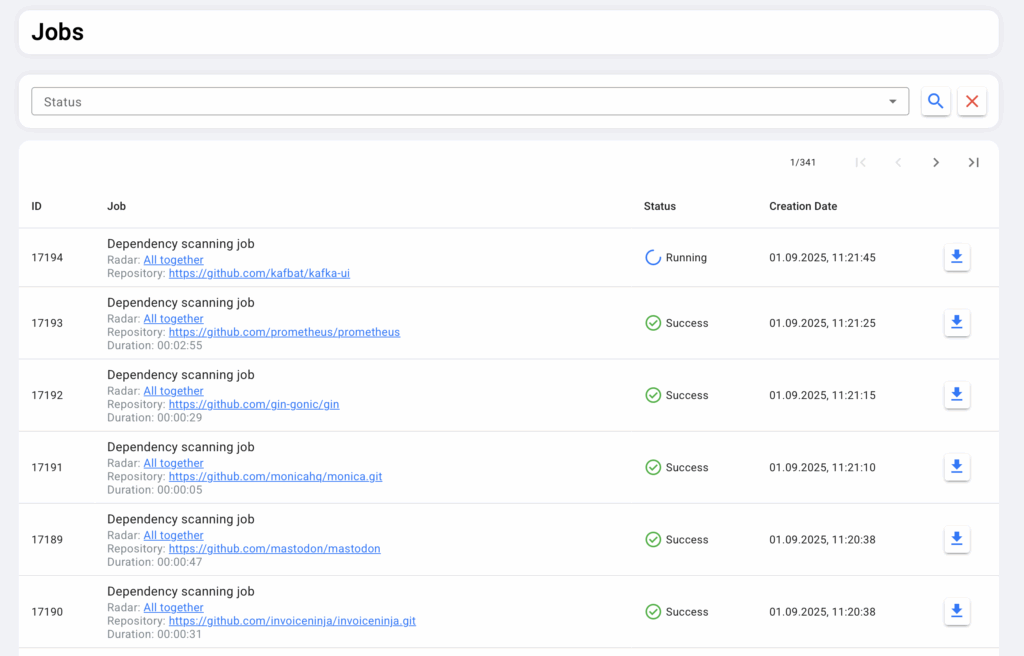
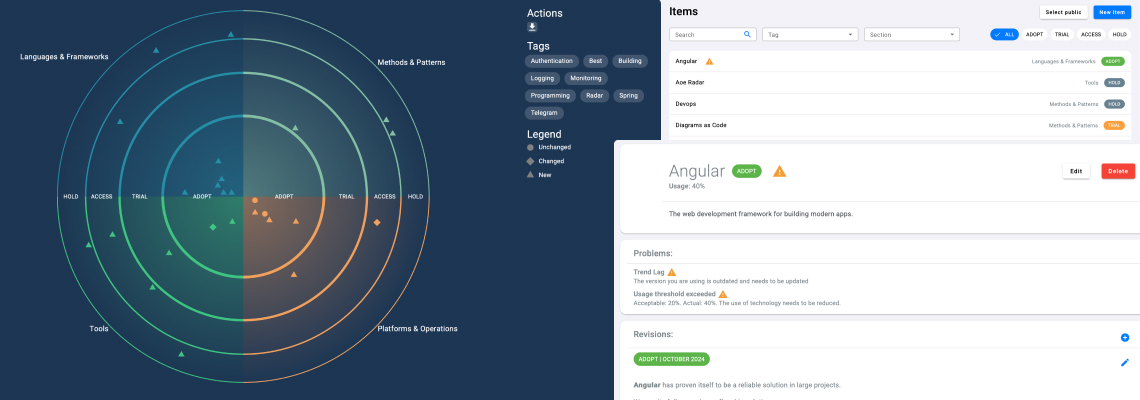
GINC RADAR подключается к git-репозиториям компании (поддерживаются GitHub, GitLab, Bitbucket и др.) и автоматически анализирует содержимое проектов. Далее радар собирает полные списки библиотек, их версии и частоту использования. Это позволяет строить карту технологий, реально задействованных в кодовой базе.
Каждая технология привязывается к своей актуальной версии. GINC RADAR показывает, насколько текущая реализация в компании отстаёт от последнего релиза. Это особенно важно для библиотек с известными уязвимостями.
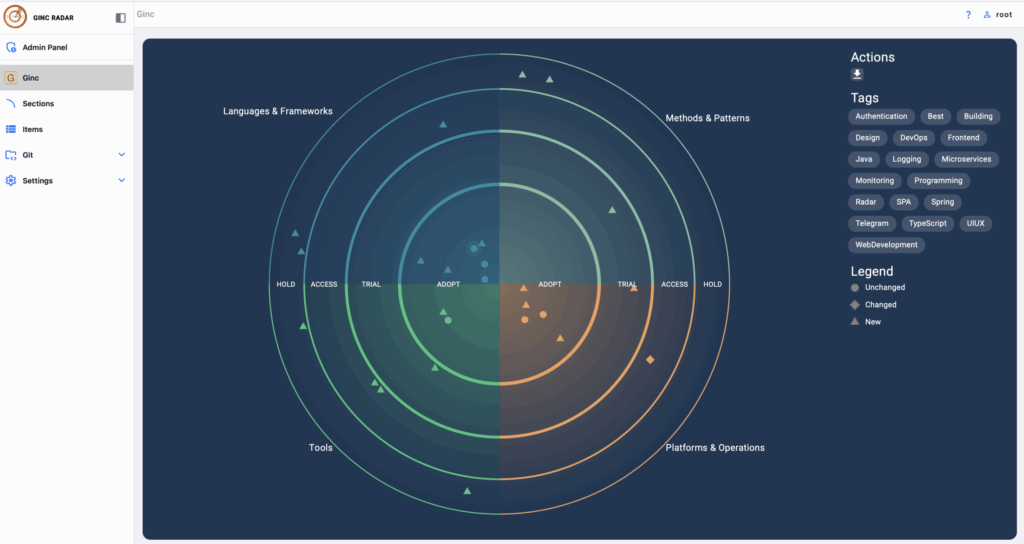
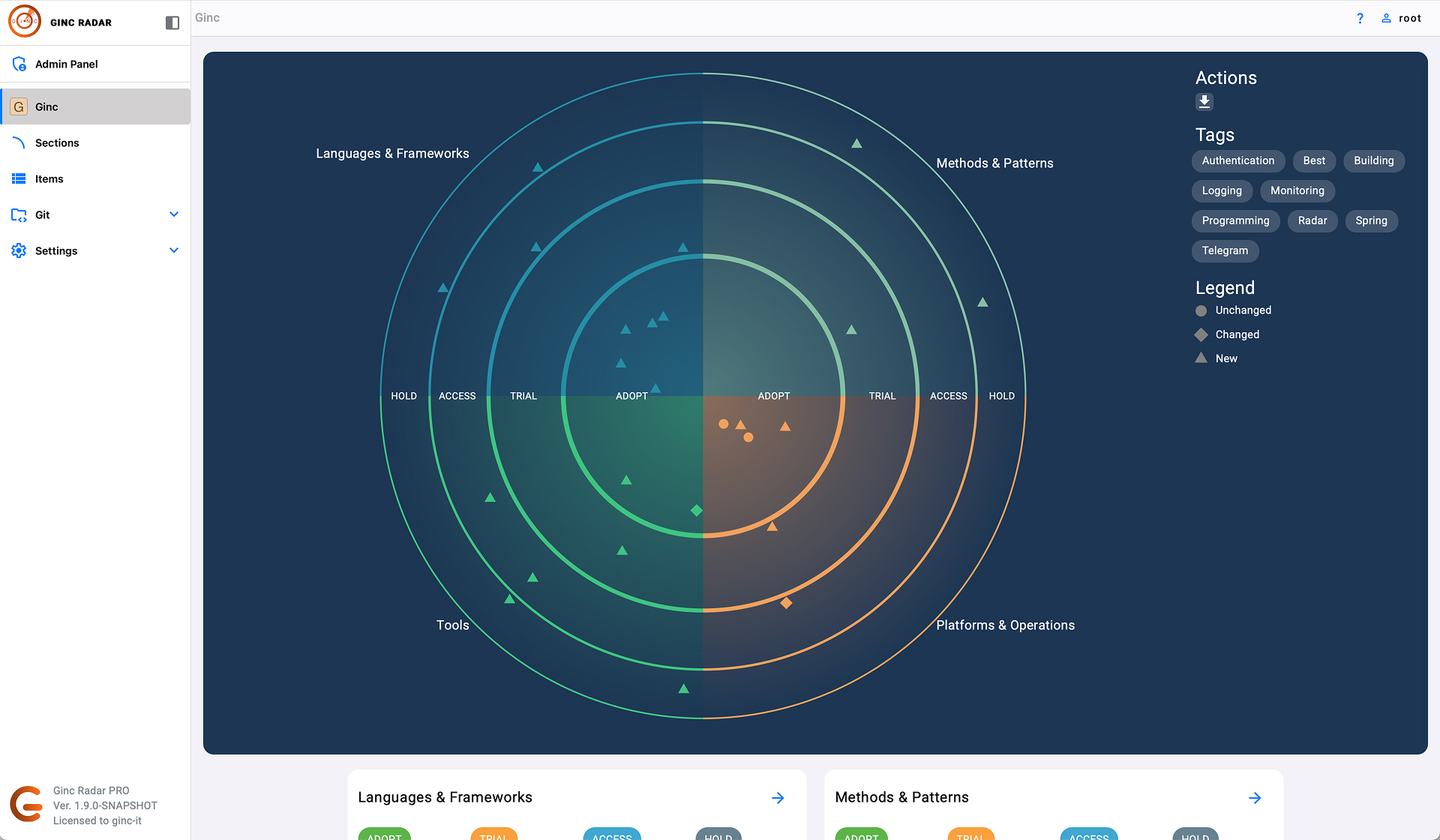
Все собранные данные выводятся на дашборд в виде радара: круговые сектора показывают тип технологий (языки, базы данных, инфраструктура, DevOps-инструменты), а кольца отражают уровень зрелости и востребованности в компании.
Архитектор или тимлид сразу видит:
какие технологии активно используются,
какие устаревают,
где есть дублирование,
какие библиотеки требуют срочного обновления.
Зачем это нужно архитекторам и тимлидам
Для архитекторов автоматическое сканирование становится способом поддерживать актуальную карту технологий без постоянных ручных проверок.
Для тимлидов это инструмент планирования миграций: видно, какие библиотеки критичны, где риски выше всего, а где обновление можно отложить.
GINC RADAR интегрируется с Jira, поэтому задачи по миграциям и обновлениям можно автоматически создавать прямо из дашборда. Это превращает “хаотичное” обновление библиотек в управляемый процесс.
Пример: как выглядит реальный кейс
Представим компанию с 50 репозиториями. Вручную составить список технологий — это минимум 2–3 недели работы нескольких инженеров. При этом через месяц часть данных устареет.
GINC RADAR подключается к тем же 50 репозиториям и за пару часов собирает статистику:
находит 120 уникальных библиотек,
определяет, что 30 % из них используют устаревшие версии,
показывает, что одна библиотека используется в 80 % проектов и требует миграции.
Вместо ручной проверки архитектор сразу получает готовую карту стека и список приоритетов.
Почему это важно для бизнеса
Автоматическое сканирование IT-инфраструктуры — это не просто удобство для инженеров. Это стратегическое преимущество для всей компании:
Снижение рисков: устаревшие компоненты не приводят к уязвимостям и сбоям.
Оптимизация расходов: дублирующие технологии можно убрать, освободив бюджет.
Прозрачность для руководства: CTO получает объективные данные, на основе которых можно планировать стратегию развития.
В эпоху, когда технологический стек компаний усложняется с каждым годом, прозрачность становится критическим фактором успеха. Ручные аудиты и Excel-таблицы больше не работают.
GINC RADAR автоматизирует процесс сканирования IT-инфраструктуры и дает архитекторам, тимлидам и CTO инструмент для принятия решений на основе данных. Это сокращает технический долг, снижает риски и делает управление технологиями прозрачным и предсказуемым.
Больше материалов

Как Ginc Radar снижает расходы на управление технологическим стеком

Почему архитекторы тратят месяцы на аудит технологий (и как это можно автоматизировать)
Как понять, что ваш технологический стек уходит в легаси — до того, как станет поздно

Ginc Radar официально в реестре российского ПО: что это значит для бизнеса?
Что такое технологический радар, и как он упрощает управление технологическим стеком